Table of Contents
Understanding Elderly Diseases: A Comprehensive Guide
Did you know that the risk of developing heart disease doubles after the age of 65? It’s a stark reminder of the health challenges many face as they grow older. Dealing with elderly diseases can be overwhelming, whether you are an elderly person or a caregiver. This post is your guide to understanding and managing these challenges. We’ll delve into common elderly diseases, exploring their symptoms, effective treatment options, and crucial preventive measures to promote a healthier and fulfilling life. This comprehensive guide explores common diseases affecting the elderly, providing insights into their symptoms, effective treatments, essential preventive measures, and how to care for loved ones.
Common Diseases in the Elderly: A Comprehensive Guide
This blog post provides a comprehensive guide to common diseases affecting the elderly. It is designed to provide information, guidance, and resources for seniors, their families, and caregivers.
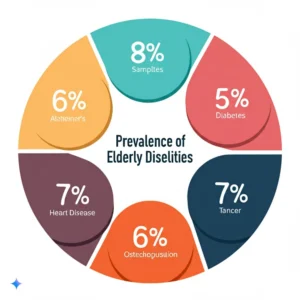
1. Overview of prevalent diseases
It’s important to understand the common diseases that affect the elderly. This section provides an overview of some major categories.
- Dementia: A general term for a decline in mental ability severe enough to interfere with daily life. This includes problems with memory, thinking, and behavior. For example, Alzheimer’s disease is the most common cause of dementia. According to the Alzheimer’s Association, nearly 1 in 10 people over 65 have Alzheimer’s disease.
- Arthritis: This is a significant cause of disability in older adults, causing joint pain and inflammation. Several types of arthritis can affect the elderly, with osteoarthritis being the most prevalent.
- Heart Disease: A broad term that encompasses conditions like coronary artery disease, heart failure, and arrhythmias. Heart disease is a leading cause of death for both men and women in the U.S., and its prevalence increases with age.
- Diabetes: Often type 2 diabetes, where the body doesn’t use insulin properly. Diabetes can lead to various complications and requires careful management.
2. Symptoms of Elderly Diseases
Early detection is crucial for effective management and treatment. Here’s what to look out for:
- Dementia: Memory loss (especially recent events), confusion, difficulty with familiar tasks, problems with language, and changes in mood or behavior.
- Arthritis: Joint pain, stiffness, swelling, warmth, and tenderness in the joints. The symptoms can vary in severity.
- Heart Disease: Chest pain (angina), shortness of breath, fatigue, and swelling in the legs or ankles.
- Diabetes: Frequent urination, excessive thirst, unexplained weight loss, blurred vision, slow-healing sores, and increased hunger.
Early Warning Signs for each Disease:
- Dementia: Misplacing items, repeating questions, and difficulty with problem-solving.
- Arthritis: Joint stiffness, especially in the mornings or after periods of inactivity.
- Heart Disease: Chest discomfort, irregular heartbeat, or unexplained fatigue.
- Diabetes: Increased thirst or urination, unexplained weight loss, and slow-healing cuts or bruises.

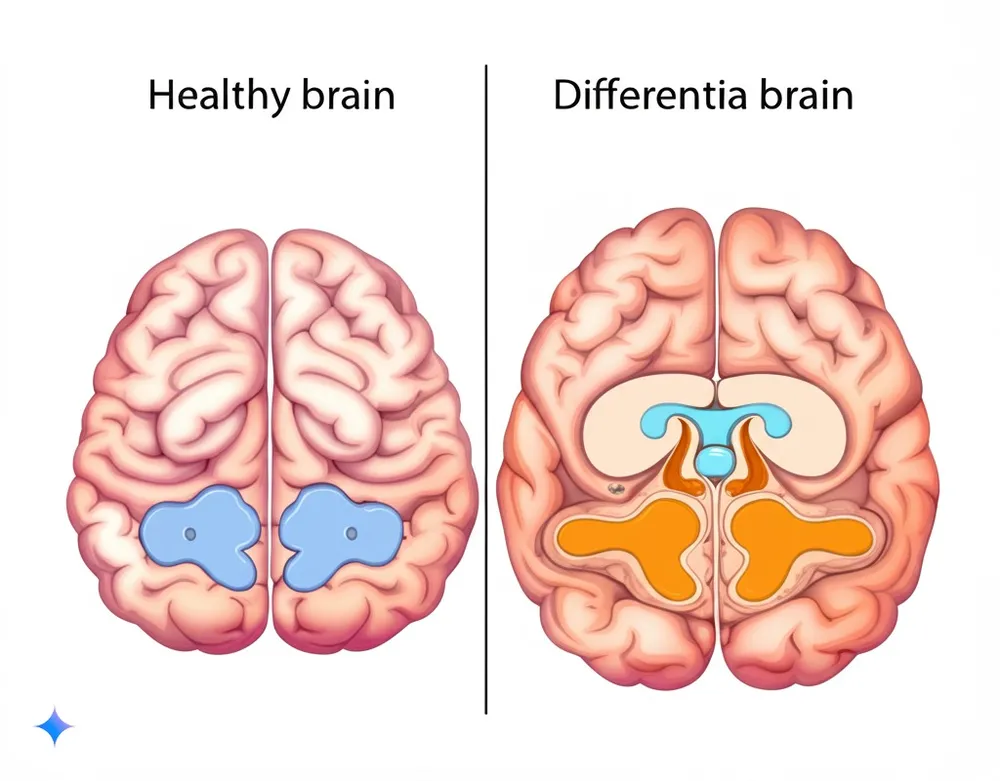
3. Dementia in the Elderly
Dementia is a serious concern for many seniors. This section delves into the different types of dementia, the symptoms, and the treatment options.
- Types of Dementia: Covering the most common types.
- Alzheimer’s disease: The most common form, characterized by progressive memory loss and cognitive decline.
- Vascular dementia: Caused by reduced blood flow to the brain, often resulting from strokes.
- Lewy body dementia: Involves fluctuations in cognitive abilities, visual hallucinations, and movement problems.
- Frontotemporal dementia: Affects the frontal and temporal lobes of the brain, leading to changes in personality and behavior.
- Symptoms: Detailed cognitive and behavioral changes.
- Cognitive: Memory loss, difficulty with problem-solving, impaired judgment, and confusion.
- Behavioral: Personality changes, agitation, wandering, and hallucinations.
- Treatment Options: Available treatments and management strategies.
- Medications: Cholinesterase inhibitors and memantine may help manage symptoms.
- Therapies: Cognitive stimulation therapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Creating a safe and structured environment, establishing routines, and providing memory aids.
4. Arthritis in the Elderly
Arthritis can severely impact the quality of life for seniors. Understanding different types, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial.
- Types of Arthritis: Highlighting the distinctions between each type.
- Osteoarthritis: The most common type, caused by the breakdown of cartilage in the joints.
- Rheumatoid arthritis: An autoimmune disease that causes inflammation and pain in the joints.
- Symptoms: How arthritis directly affects daily life.
- Joint pain, stiffness, swelling, and reduced mobility.
- Pain may worsen with activity and improve with rest.
- Treatment Options: Medications, therapies, and alternative approaches.
- Medication: NSAIDs, corticosteroids, and DMARDs for inflammation and pain.
- Physical Therapy: Exercises to improve joint function, strength, and flexibility.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Weight management, using assistive devices, and avoiding activities that aggravate symptoms.
- Alternative Therapies: Heat or cold therapy, acupuncture, and massage.

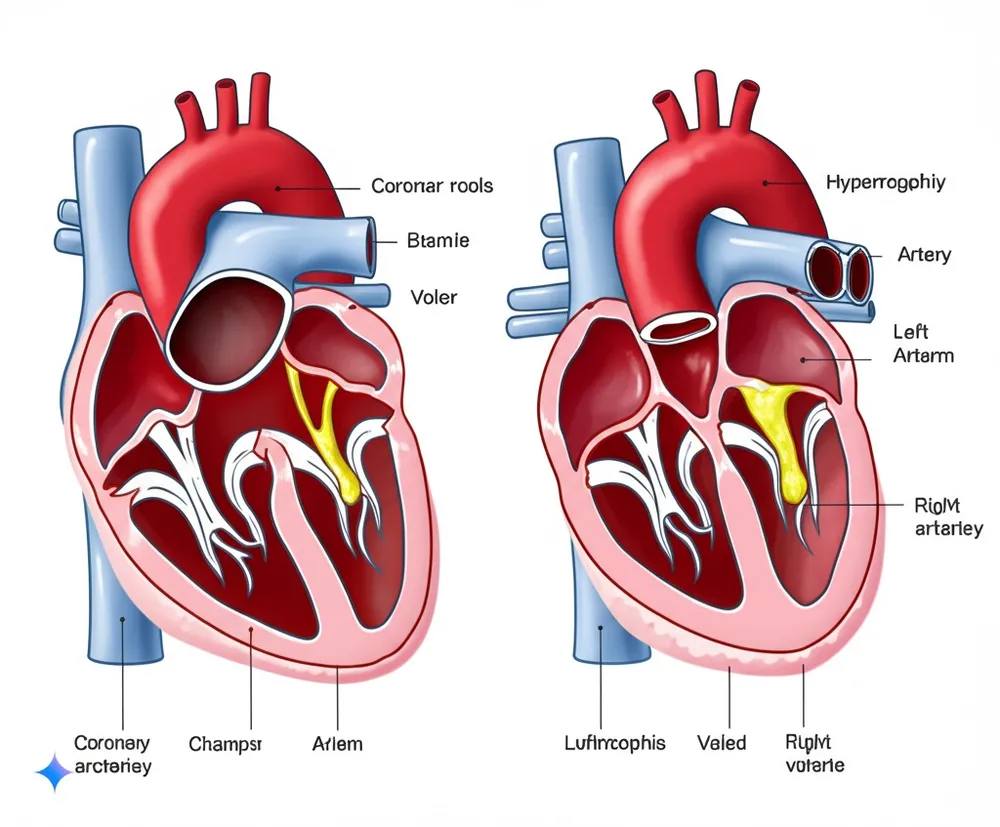
5. Heart Disease in the Elderly
Heart disease is a significant health concern for seniors. This section provides important insights into its different forms, symptoms, and treatment options.
- Types of Heart Disease: A breakdown of different heart conditions.
- Heart Failure: The heart doesn’t pump blood effectively.
- Coronary Artery Disease: A build-up of plaque in the arteries, reducing blood flow to the heart.
- Arrhythmias: Irregular heart rhythms.
- Valvular Heart Disease: Problems with the heart valves.
- Symptoms: Recognizing how heart disease presents in the elderly.
- Chest pain (angina), often described as pressure or tightness.
- Shortness of breath, especially during exertion or while lying down.
- Fatigue, even after rest.
- Swelling in the legs or ankles (edema).
- Treatment Options: Medical interventions, rehabilitation, and lifestyle improvements.
- Medical Interventions: Medications, angioplasty, bypass surgery, and implantable devices.
- Rehabilitation: Cardiac rehabilitation programs for exercise, education, and support.
- Lifestyle Changes: Diet, exercise, smoking cessation, and stress management.
6. Diabetes in the Elderly
Diabetes requires careful management, especially in the elderly. Here’s a closer look:
- Types of Diabetes: Focusing on Type 2 and its impact.
- Type 2 diabetes: The most common form, where the body either doesn’t produce enough insulin or can’t effectively use the insulin that’s produced.
- It is essential to note that in elderly individuals it is important to monitor blood sugar levels.
- Symptoms: Specific signs and potential complications.
- Frequent urination, especially at night.
- Excessive thirst.
- Blurred vision.
- Slow-healing sores and frequent infections.
- The risk of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) and hyperglycemia (high blood sugar).
- Treatment Options: Including medication, diet, and exercise strategies.
- Medication: Oral medications (e.g., metformin, sulfonylureas, etc.) and insulin injections.
- Diet: Low-glycemic-index foods, portion control, and regular meal times. Avoiding sugary drinks and processed foods.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity, such as walking or swimming.

7. Preventing Age-Related Diseases
Preventive strategies can reduce the risk of developing these diseases. Focus on proactive steps to reduce disease risk:
- Healthy Diet: Focus on nutrition for the elderly.
- Balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein.
- Portion control and calorie management.
- Key nutrients: Calcium, vitamin D, B12, and fiber.
- Exercise: Recommend suitable physical activities.
- Strength training to maintain muscle mass.
- Balance exercises to prevent falls.
- Aerobic activities like walking, swimming, or cycling.
- Exercises should be tailored to each individual’s mobility levels.
- Regular Check-ups: Emphasize the importance of medical screenings.
- Blood pressure and cholesterol checks.
- Cancer screenings (mammograms, colonoscopies, etc.).
- Eye exams and dental check-ups.
8. Best Treatments for Elderly Diseases
Explore various treatment options, including both medical and alternative approaches.
- Medical Treatments: Discuss medications and therapies for each of the diseases mentioned.
- Review medications and therapies for each disease.
- Provide updated information on medical treatments.
- Alternative Therapies: Incorporate non-pharmacological treatments.
- Physical therapy and occupational therapy to improve mobility and function.
- Complementary therapies such as acupuncture and therapeutic massage.
- Include warnings about making any medical claims.
- Caregiving: Discuss various caregiving aspects to help the patients.
- Responsibilities such as medication management.
- Help with daily tasks.
- How to provide emotional support.
- Find a local physical therapist
9. Elderly Disease Prevention Tips
Presents practical advice:
- Lifestyle: Discuss aspects of diet, exercise, and social engagement.
- Diet: Emphasize a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Provide specific examples of foods to include and avoid.
- Exercise: Recommend regular physical activity appropriate for the elderly, such as walking, swimming, or chair exercises. Define the correct amount of exercise.
- Social Engagement: Highlight the importance of staying connected with friends and family. How to foster social interactions, and how to encourage elderly people to attend group activities.
- Early Detection: Explain how to recognize early symptoms in addition to what was covered earlier.
- Early diagnosis and treatment can often slow the progression of the disease. Discuss what to do when symptoms appear.
- Support Systems: Discuss strategies to help elderly people.
- Emphasize the role of family and community support in managing chronic diseases.
- Explain the importance of joining support groups and accessing community resources.
10. How to Care for Someone with Elderly Diseases
Offers caregiving tips and assistance:
- Communication: Provide tips for effective communication.
- Be a good listener, and practice patience. Try to give clear and concise instructions.
- Daily Care: Explain how to deal with daily activities.
- Medication management, personal hygiene, and mobility assistance. Meal preparation assistance.
- Emotional Support: Provide caregivers with resources, such as support groups and counseling.
- Address the emotional toll on caregivers.
- Help caregivers implement self-care practices.

Conclusion
Caring for the elderly involves understanding and managing age-related diseases. By focusing on early detection, proper treatment, preventative measures, and supportive care, it is possible to enhance their quality of life. Regular check-ups, healthy lifestyles, and strong support systems are essential, and caregivers play a vital role in providing physical, emotional, and practical support. With the appropriate tools and guidance, seniors can live full and meaningful lives despite the challenges of aging. Consider adding links to more resources and information, and encourage readers to share the article with those who could find it useful.
Disclaimer: This blog post is intended for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice. Always consult with a healthcare professional for any health concerns or before making any decisions related to your health or treatment.
Conclusion:
- Recap: This guide has explored various aspects of elderly diseases, from understanding common conditions and recognizing early symptoms to examining effective treatment options and preventive strategies. We’ve emphasized the importance of early detection, proactive healthcare management, and the crucial role of a supportive environment in enhancing the quality of life for seniors. Empowering yourself with knowledge is the first step towards better health. If you’re seeking more personalized advice or information, we encourage you to visit our website NEEDNURSEGROUP for resources on elderly care and services. You can also contact us directly at [insert contact information] for any specific questions or concerns. Share this information with your network to help others!
- Final Thought: Navigating the complexities of elderly diseases requires a blend of awareness, compassion, and proactive care. By focusing on preventative measures, seeking timely medical interventions, and fostering a supportive community, we can significantly improve the health and well-being of our seniors, ensuring they lead fulfilling and dignified lives.





